How to read a transformer nameplate (power transformer)
Hi guys. Welcome to electrical tutorials. Today we’ll be looking at how to effectively read and interpreter the details from a power transformer.
A power transformer popularly known as a transformer is a passive electrical device use to alter voltage. That means a transformer can either step down voltage levels or step-up voltage levels.
Unlike instrument transformer, it’s primary function is not for protection and metering.
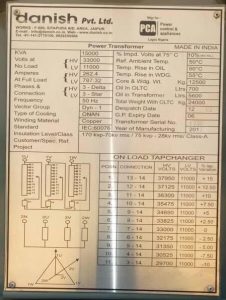
In the picture above, you’ll see a typical transformer nameplate. We’ll be using the details from this nameplate to exhaust what each and every term in the nameplate means.
Before we dive into that, it is worthy to note that a transformer can either be a step-up transformer or step down transformer, not both. This is to say you can wire any transformer to either act as a step-up transformer or step down transformer.
How to do that will be discussed another day. Now, let’s cut to the chase.
KVA: 15000
This is the rated capacity of the power transformer. From the picture above, this transformer has a rated capacity of 15000KVA.
Volts at no load
HV: 33000volts
The rated voltage for the high voltage side of the transformer under no-load condition is 33 000volts
LV: 11000volts
The rated voltage for the low voltage side of the transformer under no-load condition is 11 000volts
Amperes at full load
HV: 262.4
The full load rated current capacity for the high voltage side is 262.4Amperes
LV: 787.32
The full load rated current capacity for the low voltage side is 787.32Amperes
Phases and connection
HV: 3-delta
The high voltage side has 3 phases with delta connection
LV: 3-star
The low voltage side has 3 phases with star connection
Frequency: 50Hz
This means the frequency for both the high voltage and low voltage side of the transformer is 50Hz
Vector group: Dyn-1
This is talking about the winding connection of the transformer which is Dyn-1
D- delta connection
y- star connection
n- neutral connection
1- The phase shift 30 degree clockwise.
Here, the vector group mentions that the High voltage will be shifted by 30 degrees in the low voltage side. Mostly used in step down transformer to compensate for transformation ratio
Type of cooling: ONAN
Oil natural Air natural (ONAN). This means that this transformer will be cooled by the transformer wings and open air.
Winding material: Copper
This means the material used for the winding of a transformer is copper
Standard: IEC:60076
This means that this transformer is manufactured and tested in accordance to IEC:60076 standards
Insulation level/class customer/Spec. Ref. Project: 170kvp-70kv rms/75kvp-28kv rms/class-A
This is the dielectric strength of the insulation under various voltage level. The type of transformer insulation used.
% impd. volts at 75°c: 10%
The % impedance voltage at 75°C is 10%. That means the impedance of the winding referred to one side of the transformer is 10%. If the transformer is loaded 100%, the output voltage will be decreased by 10%.
Ref. Ambient Temp: 50°c
This means the air temperature surrounding the transformer is 50%.
Temp. rise in OIL: 50°c
This means the highest permissible temperature rise in oil is 50°c.
Temp. rise in WDG.: 55°c
This means the highest permissible temperature rise in the winding is 55°c.
Core and Wdg. Wt. (kg): 12500
This means the core and winding weight of the transformer is 12500Kg.
Oil in OLTC (Ltrs.): 700
This means that the oil in the on-load tap changer (OLTC) is 700litres.
Oil in Transformer (Ltrs.): 5600
This means that the volume of oil in the transformer is 5600litres.
Total weight with OLTC (Kg): 24000
This means the total with the on line tap changer is 24000Kg.
Dispatch date
This is the date the upon which the transformer is physically loaded to a tractor.
G.P expiry date
This is the last day the transformer is safe to be used.
Transformer serial No.
This represents the serial number of the transformer
Year of manufacturing: 2012
This means the transformer was manufactured in 2012
ON LOAD TAPCHANGER
This is used to increase or decrease the transformation ratio of the transformer
How to read a current transformer (CT) nameplate
How to effectively install a stay on a pole
Electrical overhead line materials and functions (33kv and 11kv)
Substation layout design consideration
How to effectively install thunder arrestor in Nigeria
[…] How to read a transformer nameplate (power transformer) […]